Services is the Android component which is used to perform long-running background tasks. There are other Android components which run in the background too, like Broadcast receiver and JobScheduler, but they are not used for long running tasks. Matter of fact, a broadcast receiver, though runs in the background, need to exit the onReceive method within 10 seconds or else Android will kill it. JobScheduler, also runs in the background, is used for batching the background tasks.
So generally speaking, Services are the components you should go to if you want to keep something running in the background well beyond the lifecycle of the activity. Now there are some cases where you would want to run the services for as long as other components want. Let’s say you are using a service which generates a random number every few seconds and your activity displays that number. In this case, running a service beyond the activity’s life doesn’t make sense (as there is no one else to consume the random number).
Also, since you need to communicate with the service by asking “Hey, what’s the generated random number again?”, you need a way to communicate with the service component that runs in the background.
Finally, when the activity destroys, you need to dispose of the service so that it’s not running in the background indefinitely(or the system destroys it).
This kind of services, which runs in the background, has an interface with which other components can communicate, and extends up to the time till other components decide otherwise, is known as bound services.
A very common example of a bound service is a JobService class from the JobScheduler API. The JobService is bound to the system, enabling the system to call its methods like onStartJob and is unbound when the job has stopped executing.
In this post, we will explore bound services using a sample app.
The sample app
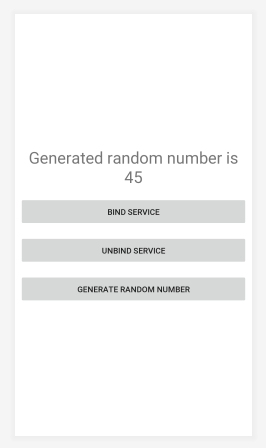
Below is the screen of a simple app that we’ll be developing for this post. The buttons are self-explanatory. The “Generate random number” button will ask the bouned service about the generated random number and will show it in the text field above. Below is an image of screen of our app.
 You can get the entire source code at the Github repository
You can get the entire source code at the Github repository
The plan
Since we saw that in bound services we can make method calls on the service, it is fairly obvious that we need a reference of the service in order to make method calls on it. So the first step will be to implement the onBind method of the service, which we will use to get the reference of the service.
Then we will need to create a ServiceConnection object and the binding component will use it to bind with the service. A ServiceConnection object links the service with the component and service’s lifecycle is bound to that ServiceConnection. When you implement ServiceConnection, you will need to implement two methods i.e. onServiceConnected and onServiceDisconnected. In the onServiceConnected, we will initialize our service reference and then we can make method calls on the service.
When we have our ServiceConnection object made, we will use the bindService method to connect all the components (i.e. the activity with the service) and create the service. This will also take service connection object as an argument.
Don’t worry if anything is confusing at the moment, we will work together on the app now to clear out the things.
Provide support of binding for the service.
First, we will support binding for the service(let’s name the service RandomNumberGeneratorService). In order to do so, we need to implement the onBind method. This method returns an IBinder reference, so we will need to have a class (let’s name it RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder) of type IBinder. There are two ways to go about that. You can either implement the IBinder on the RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder class, or you can extend it using Binder abstract class. The Binder abstract class implements the IBinder interface.
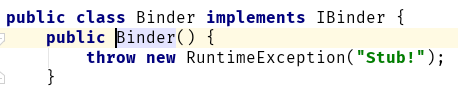
We will then create a property inside the RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder class named service which will return the service. Here is how our RandomNumberGeneratorService looks so far:
class RandomNumberGeneratorService:Service() {
val binder: IBinder = RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder()
inner class RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder : Binder(){
val service: RandomNumberGeneratorService = this@RandomNumberGeneratorService
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent): IBinder {
return binder
}
}
ServiceConnection
Simply put, a connection between the service and the component is called a ServiceConnection. In order to bind the service with a component, we need to override the onServiceConnected and onServiceDisconnected methods. As stated before, in the onServiceConnected method, we will get the reference of the service.
Here is how our code looks. In our case, the activity is the component that is trying to bind to the service, hence we’ve created a ServiceConnection object there.
var randomNumberGeneratorService: RandomNumberGeneratorService? = null
private lateinit var connection: ServiceConnection
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
connection = object : ServiceConnection{
override fun onServiceDisconnected(componentName: ComponentName) {
randomNumberGeneratorService = null
}
override fun onServiceConnected(componentName: ComponentName
, service: IBinder) {
randomNumberGeneratorService = (service as RandomNumberGeneratorService.RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder).service
}
}
setupViews()
}
Now that we have everything set up, we can finally bind to service. We can use the bindService method which takes an intent, service connection object and a flag.
bindService(Intent(this, RandomNumberGeneratorService::class.java),connection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE)
BIND_AUTO_CREATE - This flag is used in cases where service’s lifetime is valid till all the clients bound to it. The service will be destroyed as soon as all the clients unbind from it. This flag is not recommended if you plan to start a service and decide to bind to it later.
We are also generating random numbers in the service and we can get that number using a property call randomNumber. Here is how our service looks now:
class RandomNumberGeneratorService:Service() {
private val HANDLER_THREAD_NAME="random_number_generator_thread"
val binder: IBinder = RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder()
lateinit var handlerThread:HandlerThread
lateinit var handler: Handler
var randomNumber: Int = -1
private val TAG = RandomNumberGeneratorService::class.java.simpleName
inner class RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder : Binder(){
val service: RandomNumberGeneratorService = this@RandomNumberGeneratorService
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent): IBinder {
return binder
}
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
mNM = getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE) as NotificationManager;
Log.d(TAG,"service created")
handlerThread = HandlerThread(HANDLER_THREAD_NAME)
handlerThread.start()
handler = Handler(handlerThread.looper)
handler.post {
startGeneratingRandomNumber()
}
showNotification()
}
lateinit var mNM: NotificationManager
private val NOTIFICATION = R.string.local_service_started
lateinit var notificationBuilder: NotificationCompat.Builder
private fun showNotification() {
val text = getText(R.string.local_service_started)
// The PendingIntent to launch our activity if the user selects this notification
val contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(
this, 0,
Intent(this, MainActivity::class.java), 0
)
// Set the info for the views that show in the notification panel.
notificationBuilder = NotificationCompat.Builder(this)
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) // the status icon
.setTicker(text) // the status text
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis()) // the time stamp
.setContentTitle(getText(R.string.local_service_started)) // the label of the entry
.setContentText(text) // the contents of the entry
.setContentIntent(contentIntent) // The intent to send when the entry is clicked
// Send the notification.
mNM.notify(NOTIFICATION, notificationBuilder.build())
}
override fun onDestroy() {
generateRandomNumber = false
handler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(null)
handler.looper.quit()
handlerThread.quit()
mNM.cancel(NOTIFICATION)
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
return START_NOT_STICKY
}
var generateRandomNumber = false
private fun startGeneratingRandomNumber() {
generateRandomNumber = true
while (generateRandomNumber){
Thread.sleep(1000)
randomNumber = (Math.random()*100).toInt()
}
}
}
We are using a HandlerThread to generate random number because we are doing it at an interval of 1 second and we don’t want to put main thread to sleep(Services run on main thread) when we use Thread.sleep() method.
When we bind a service, we can see a small notification on top.
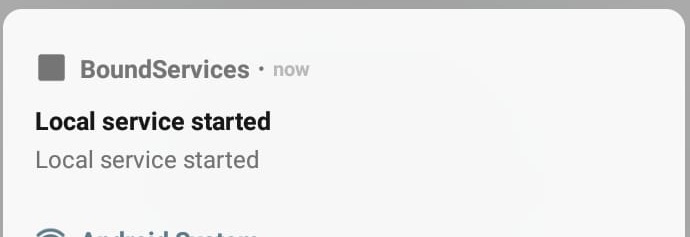 When we have bound to that service, we can get the random number by pressing the “Get random number button”
When we have bound to that service, we can get the random number by pressing the “Get random number button”
Now you are communicating with the bound service, which is the purpose of this kind of services.
We can use “Unbind service” to unbind from the running service. The unbindService method just takes the service connection object.
Here is how our activity(the component which binds to the service) code.
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
var randomNumberGeneratorService: RandomNumberGeneratorService? = null
private lateinit var connection: ServiceConnection
var bounded = false
val TAG = MainActivity::class.java.simpleName
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
connection = object : ServiceConnection{
override fun onServiceDisconnected(componentName: ComponentName) {
Log.d(TAG,"Service disconnected.")
randomNumberGeneratorService = null
}
override fun onServiceConnected(componentName: ComponentName
, service: IBinder) {
Log.d(TAG, "Service connected.")
randomNumberGeneratorService = (service as RandomNumberGeneratorService.RandomNumberGeneratorServiceBinder).service
}
}
setupViews()
}
private fun setupViews() {
bind_service.setOnClickListener {
if(!bounded){
bindService(Intent(this, RandomNumberGeneratorService::class.java),connection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE)
bounded = true
}
}
get_random_number.setOnClickListener {
if(!bounded){
generated_random_number.text = getString(R.string.service_not_bound)
}else{
generated_random_number.text = randomNumberGeneratorService?.randomNumber.toString()
}
}
unbind_service.setOnClickListener {
unbindSafely()
}
}
private fun unbindSafely() {
if (bounded) {
unbindService(connection)
bounded = false
}
}
override fun onDestroy() {
unbindSafely()
super.onDestroy()
}
}
Note that we have used a boolean bounded to keep track of the bind state of the service. If you try to unbound a service which wasn’t bound(or was unbounded) previously, you get an exception java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Service not registered:
Also, update the bounded variable after pressing the “Unbind service” button. Don’t rely on onServiceDisconnected method for that. That method is not called when you call unbindService. That method will only be called in case the connection between your service and ServiceConnection is dropped.
Few things to note:
- Note that if the service was created using
bindServicemethod, it is destroyed when all the components unbind from it. In our case, the service is destroyed when we unbind from it. - You can start a service using
startServicemethod and bind to it later too. In this case, if you bind to this service later, callingunbindServicewill not destroy it. You’ll have to usestopServiceorstopSelfmethods. - If you connected to a running Service using the BIND_AUTO_CREATE , and you call stopService, the Service will not stop until all these clients have unbound.
- When the service’s lifecycle makes sense only when the activity is in visible state, you should bind in the
onStartmethod and unbind in theonStopmethod of the activity. - If you create a thread in the service, it will continue to run even after you unbind from it. So it’s important to stop the thread to conserve resources.
You can get the entire source code from the Github repository(https://github.com/aanandshekharroy/bound-services-demo.git)